Categories
-
Advertising / Agriculture / Apparel & Clothing
-
Architecture / Art & Craft / Automobiles
-
Bags & Shoes Accessories / Spare Parts / Books & Stationery
-
Business Services / Mobile Accessories / Computers & Laptops
-
Construction / Contractors & Freelancers / Education & Training
-
Electronics / Engineering / Environment
-
Event Planner / Fashion & Beauty / Financial
-
Gifts & Toys / Handicrafts / Health Care
-
Home Appliances / Hotel & Restaurants / Industrial Chemicals
-
Machinery Equipment / Information Technology / Jewelry
-
Kitchen / Instruments / Leather
-
Packaging / Personal / Plastic Products
-
Recruitment / Rental / Restaurants & Beverages
-
Security / Telecommunication / Tour & Travels
-
Transportation / Wooden Furniture
Intermediates
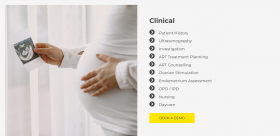
Business Services - Industrial services-
*******041
Show
- Supplier: Matangi Industries
- Price: N/A
- Add to Favourite








































 get multiple quotes
get multiple quotes